In the continuation of the last blog Web Application Architecture Part-1 (Guide to Become Full Stack Developer), this article will cover more detailed information on some common types of Web Application Architecture.
As we have discussed in the last part that there are different approaches to creating a structural design and all that depends on the scope of work and the area of work (Like e-Commerce, Chat Applications, etc). This post is going to highlight some of the modern design architecture with the desired functionality and quality attributes. Hence, we should understand different architectures, before applying them to our design.
So let’s begin with the most commonly known architectural design:
1. Client-Server Architecture
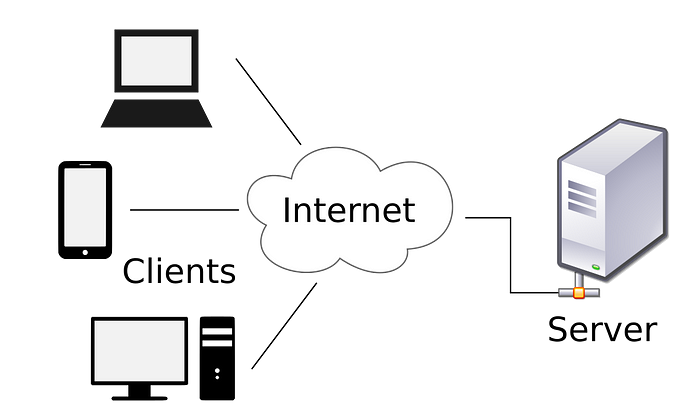
Client-server architecture (client/server) is a network architecture in which each computer or process on the network is either a client or a server.
Servers are powerful computers or processes dedicated to managing disk drives (file servers), printers (print servers), or network traffic (network servers).
Clients are PCs or workstations on which users run applications. Clients rely on servers for resources, such as files, devices, and even processing power.
Area of use: Online promotional website, email, document sharing, and banking
2. MVC Architecture
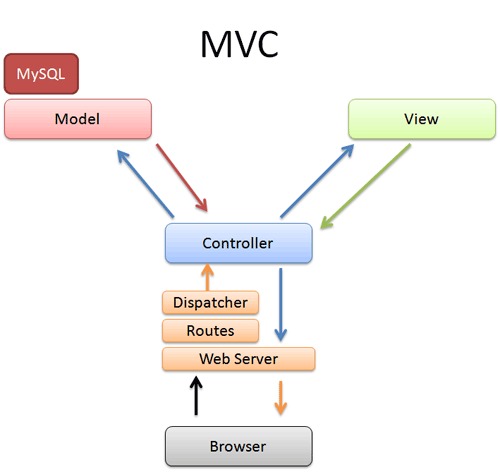
The MVC architectural pattern has existed for a long time in software engineering. Mostly all of the coding languages use MVC with slight variation, but conceptually it remains the same.
MVC stands for Model, View, and Controller. The MVC model separates the application into these three components — Model, View, and Controller.
The model is data and logic.
The model represents the shape of the data and logic. It maintains the data of the application. Model objects retrieve and store model state in a database.
The view is a User Interface.
The view displays data using the model to the user and also enables them to modify the data.
The controller is a request handler.
The controller handles the user request. Typically, a user interacts with View, which in turn raises an appropriate URL request, this request will be handled by a controller. The controller renders the appropriate view with the model data as a response.
Area of use:
- Architecture for World Wide Web applications in major programming languages
- Web frameworks such as Laravel and Adonisjs
3. Master-Slave Architecture:
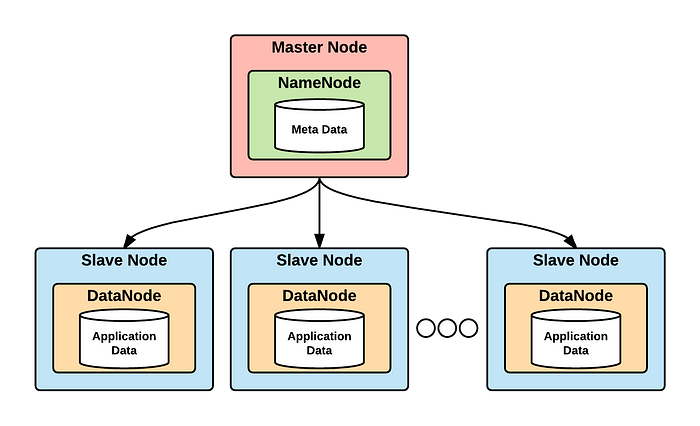
In computer science, the master/slave architecture initially started in the context of database replication.
For example, if there’s a database where data is replicated across 3 servers, there are chances that at least one of these could be out of sync with others. How to resolve the inconsistency in such cases? With the master-slave architecture, one replica is identified as the master and the others serve as slaves. The new terminology is primary vs replica (or secondary).
The same is true for web servers. When we are doing vertical scaling of the system we use a replication system, where one store the master code and the other are the replicas of that
Area of use:
- In database replication, the master database is regarded as the authoritative source, and the slave databases are synchronized to it
- Peripherals connected to a bus in a computer system (master and slave drives)
4. Broker Architecture:
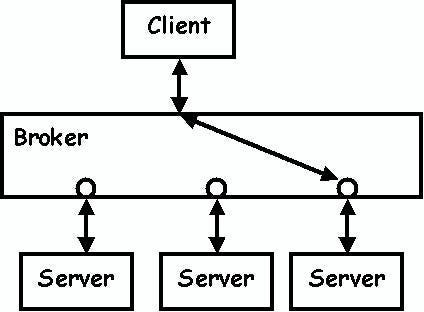
This pattern is used to structure distributed systems with decoupled components. These components can interact with each other by remote service invocations. A broker component is responsible for the coordination of communication among components.
Servers publish their capabilities (services and characteristics) to a broker. Clients request a service from the broker, and the broker then redirects the client to a suitable service from its registry.
Area of use: Message broker software such as Apache ActiveMQ, Apache Kafka, RabbitMQ, and JBoss Messaging.
5. Peer-to-peer or P2P Architecture:
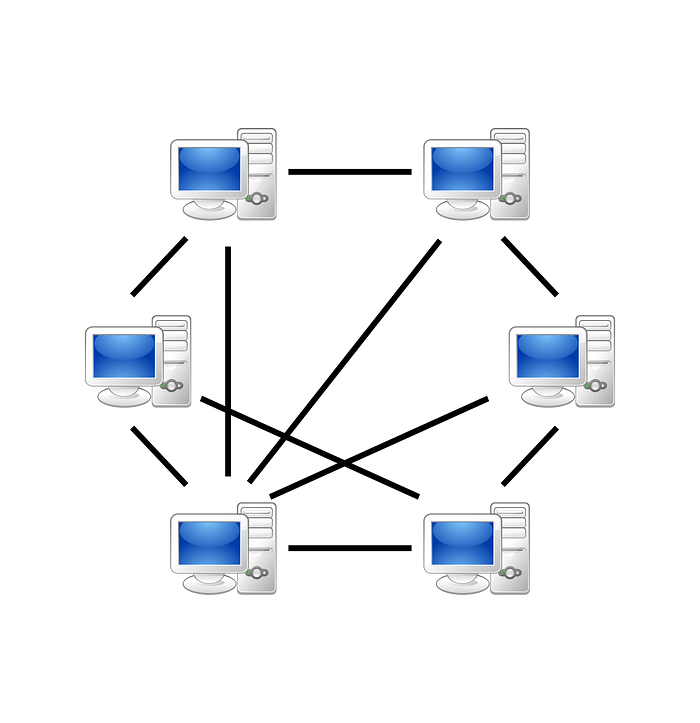

Peer-to-peer architecture (P2P architecture) is a commonly used computer networking architecture in which each workstation, or node, has the same capabilities and responsibilities. It is often compared and contrasted to the classic client/server architecture, in which some computers are dedicated to serving others.
Area of use:
- File-sharing networks such as Gnutella and G2)
- Multimedia protocols such as P2PTV and PDTP.
The above are some of the most common web application architecture patterns. We hope that by now you have got to know enough about Full stack Development and how we can use different design pattern and technologies to structure a project from scratch to final product.
In the last part of Guide to become Full Stack Developer we will discuss GIT and DevOps.